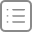
- Apk安装的主要步骤:
- 1. 将apk文件copy至
data/app目录- 1.1 installPackageAsUser
- 1.2 handleMessage(INIT_COPY)&handleMessage(MCS_BOUND)
- 1.3 HandlerParams.startCopy
- 1.4 handleStartCopy()
- 2 .解析apk信息
- 2.1 processPendingInstall()
- 2.2 installPackageLI(args, res)
- 2.3 installNewPackageLI()
- 2.4 scanPackageLI()
- 3. dexopt操作
- 3.1 performDexOptLI()
- 3.2 Installer.dexopt
- 3.3 commands::dexopt()
- 4. 更新权限信息
- 4.1 updatePermissionsLPw
- 4.2 完成安装
Apk安装的主要步骤:
为了学习这个过程,真的是陷入了pms的源码很久,也看了很多前人的博文,才算是有了些思路,所以此处先把主要步骤列出来,后面再慢慢分析细节。
- 将apk文件复制到
data/app目录 - 解析apk信息
- dexopt操作
- 更新权限信息
- 完成安装,发送
Intent.ACTION_PACKAGE_ADDED广播
下面将具体步骤列张图出来:

由图可见安装过程中流转的步骤还是比较多的,下面具体分析
1. 将apk文件copy至data/app目录
1.1 installPackageAsUser
mContext.enforceCallingOrSelfPermission(android.Manifest.permission.INSTALL_PACKAGES, null);final int callingUid = Binder.getCallingUid();......if ((callingUid == Process.SHELL_UID) || (callingUid == Process.ROOT_UID)) {installFlags |= PackageManager.INSTALL_FROM_ADB;} else {// Caller holds INSTALL_PACKAGES permission, so we're less strict// about installerPackageName.installFlags &= ~PackageManager.INSTALL_FROM_ADB;installFlags &= ~PackageManager.INSTALL_ALL_USERS;}UserHandle user;if ((installFlags & PackageManager.INSTALL_ALL_USERS) != 0) {user = UserHandle.ALL;} else {user = new UserHandle(userId);}verificationParams.setInstallerUid(callingUid);final File originFile = new File(originPath);final OriginInfo origin = OriginInfo.fromUntrustedFile(originFile);final Message msg = mHandler.obtainMessage(INIT_COPY);msg.obj = new InstallParams(origin, observer, installFlags,installerPackageName, verificationParams, user, packageAbiOverride);mHandler.sendMessage(msg);
这个方法主要是判断安装来源,包括adb,shell,all_user,然后向PMS的mHandler发送INIT_COPY的消息,这个mHandler运行在一个HandlerThread中。
1.2 handleMessage(INIT_COPY)&handleMessage(MCS_BOUND)
case INIT_COPY:{HandlerParams params = (HandlerParams) msg.obj;int idx = mPendingInstalls.size();if (DEBUG_INSTALL) Slog.i(TAG, "init_copy idx=" + idx + ": " + params);// If a bind was already initiated we dont really// need to do anything. The pending install// will be processed later on.if (!mBound) {// If this is the only one pending we might// have to bind to the service again.if (!connectToService()) {Slog.e(TAG, "Failed to bind to media container service");params.serviceError();return;} else {// Once we bind to the service, the first// pending request will be processed.mPendingInstalls.add(idx, params);}} else {mPendingInstalls.add(idx, params);// Already bound to the service. Just make// sure we trigger off processing the first request.if (idx == 0) {mHandler.sendEmptyMessage(MCS_BOUND);}}}case MCS_BOUND:{......HandlerParams params = mPendingInstalls.get(0);if (params != null) {if (params.startCopy()) {// We are done... look for more work or to// go idle.if (DEBUG_SD_INSTALL) Log.i(TAG,"Checking for more work or unbind...");// Delete pending installif (mPendingInstalls.size() > 0) {mPendingInstalls.remove(0);}if (mPendingInstalls.size() == 0) {if (mBound) {if (DEBUG_SD_INSTALL) Log.i(TAG,"Posting delayed MCS_UNBIND");removeMessages(MCS_UNBIND);Message ubmsg = obtainMessage(MCS_UNBIND);// Unbind after a little delay, to avoid// continual thrashing.sendMessageDelayed(ubmsg, 10000);}......}
INIT_COPY主要是确保DefaultContainerService已bound,DefaultContainerService是一个应用服务,具体负责实现APK等相关资源文件在内部或外部存储器上的存储工作。而MCS_BOUND中则执行了params.startCopy()这句,也是最关键的开始copy文件。
1.3 HandlerParams.startCopy
final boolean startCopy() {boolean res;try {if (DEBUG_INSTALL) Slog.i(TAG, "startCopy " + mUser + ": " + this);if (++mRetries > MAX_RETRIES) {Slog.w(TAG, "Failed to invoke remote methods on default container service. Giving up");mHandler.sendEmptyMessage(MCS_GIVE_UP);handleServiceError();return false;} else {handleStartCopy();res = true;}} catch (RemoteException e) {if (DEBUG_INSTALL) Slog.i(TAG, "Posting install MCS_RECONNECT");mHandler.sendEmptyMessage(MCS_RECONNECT);res = false;}handleReturnCode();return res;}
该方法中除了检查重试次数外只是简单的调用了handleStartCopy()及handleReturnCode()方法.
1.4 handleStartCopy()
这个方法内容非常多,下面只列出些核心部分
public void handleStartCopy() throws RemoteException {int ret = PackageManager.INSTALL_SUCCEEDED;......final boolean onSd = (installFlags & PackageManager.INSTALL_EXTERNAL) != 0;final boolean onInt = (installFlags & PackageManager.INSTALL_INTERNAL) != 0;PackageInfoLite pkgLite = null;if (onInt && onSd) {// Check if both bits are set.Slog.w(TAG, "Conflicting flags specified for installing on both internal and external");ret = PackageManager.INSTALL_FAILED_INVALID_INSTALL_LOCATION;} else {pkgLite = mContainerService.getMinimalPackageInfo(origin.resolvedPath, installFlags,packageAbiOverride);/** If we have too little free space, try to free cache* before giving up.*/if (!origin.staged && pkgLite.recommendedInstallLocation== PackageHelper.RECOMMEND_FAILED_INSUFFICIENT_STORAGE) {final StorageManager storage = StorageManager.from(mContext);final long lowThreshold = storage.getStorageLowBytes(Environment.getDataDirectory());final long sizeBytes = mContainerService.calculateInstalledSize(origin.resolvedPath, isForwardLocked(), packageAbiOverride);if (mInstaller.freeCache(sizeBytes + lowThreshold) >= 0) {pkgLite = mContainerService.getMinimalPackageInfo(origin.resolvedPath,installFlags, packageAbiOverride);}}}......* No package verification is enabled, so immediately start* the remote call to initiate copy using temporary file.*/ret = args.copyApk(mContainerService, true);}mRet = ret;}
handleStartCopy的核心就是copyApk,其他的都是些存储空间检查,权限检查等等安全校验
2 .解析apk信息
完成apk copy到data/app目录的操作后,下一步就到了 handleReturnCode,这个方法又跳转到processPendingInstall()方法,下面先来看看processPendingInstall()方法:
2.1 processPendingInstall()
private void processPendingInstall(final InstallArgs args, final int currentStatus) {// Queue up an async operation since the package installation may take a little while.mHandler.post(new Runnable() {public void run() {mHandler.removeCallbacks(this);// Result object to be returnedPackageInstalledInfo res = new PackageInstalledInfo();res.returnCode = currentStatus;res.uid = -1;res.pkg = null;res.removedInfo = new PackageRemovedInfo();if (res.returnCode == PackageManager.INSTALL_SUCCEEDED) {args.doPreInstall(res.returnCode);synchronized (mInstallLock) {installPackageLI(args, res); //1.安装}args.doPostInstall(res.returnCode, res.uid);}// A restore should be performed at this point if (a) the install// succeeded, (b) the operation is not an update, and (c) the new// package has not opted out of backup participation.final boolean update = res.removedInfo.removedPackage != null;final int flags = (res.pkg == null) ? 0 : res.pkg.applicationInfo.flags;boolean doRestore = !update&& ((flags & ApplicationInfo.FLAG_ALLOW_BACKUP) != 0);// Set up the post-install work request bookkeeping. This will be used// and cleaned up by the post-install event handling regardless of whether// there's a restore pass performed. Token values are >= 1.int token;if (mNextInstallToken < 0) mNextInstallToken = 1;token = mNextInstallToken++;PostInstallData data = new PostInstallData(args, res);mRunningInstalls.put(token, data);if (DEBUG_INSTALL) Log.v(TAG, "+ starting restore round-trip " + token);if (res.returnCode == PackageManager.INSTALL_SUCCEEDED && doRestore) {// Pass responsibility to the Backup Manager. It will perform a// restore if appropriate, then pass responsibility back to the// Package Manager to run the post-install observer callbacks// and broadcasts.IBackupManager bm = IBackupManager.Stub.asInterface(ServiceManager.getService(Context.BACKUP_SERVICE));if (bm != null) {if (DEBUG_INSTALL) Log.v(TAG, "token " + token+ " to BM for possible restore");try {bm.restoreAtInstall(res.pkg.applicationInfo.packageName, token); //2.调用backup服务} catch (RemoteException e) {// can't happen; the backup manager is local} catch (Exception e) {Slog.e(TAG, "Exception trying to enqueue restore", e);doRestore = false;}} else {Slog.e(TAG, "Backup Manager not found!");doRestore = false;}}if (!doRestore) {// No restore possible, or the Backup Manager was mysteriously not// available -- just fire the post-install work request directly.if (DEBUG_INSTALL) Log.v(TAG, "No restore - queue post-install for " + token);Message msg = mHandler.obtainMessage(POST_INSTALL, token, 0);mHandler.sendMessage(msg);}}});}
这个方法有几个关键步骤,一是installPackageLI(args, res);,这个方法具体执行了解析package和后续操作,而再installPackageLI(args, res);执行完毕后会走到bm.restoreAtInstall(res.pkg.applicationInfo.packageName, token);,会调用backupservice的restoreAtInstall方法,而restoreAtInstall方法最终又会调用PMS的finishPackageInstall()方法,完成安装。
2.2 installPackageLI(args, res)
private void installPackageLI(InstallArgs args, PackageInstalledInfo res) {final int installFlags = args.installFlags;String installerPackageName = args.installerPackageName;File tmpPackageFile = new File(args.getCodePath());boolean forwardLocked = ((installFlags & PackageManager.INSTALL_FORWARD_LOCK) != 0);boolean onSd = ((installFlags & PackageManager.INSTALL_EXTERNAL) != 0);boolean replace = false;final int scanFlags = SCAN_NEW_INSTALL | SCAN_FORCE_DEX | SCAN_UPDATE_SIGNATURE;// Result object to be returnedres.returnCode = PackageManager.INSTALL_SUCCEEDED;if (DEBUG_INSTALL) Slog.d(TAG, "installPackageLI: path=" + tmpPackageFile);// Retrieve PackageSettings and parse packagefinal int parseFlags = mDefParseFlags | PackageParser.PARSE_CHATTY| (forwardLocked ? PackageParser.PARSE_FORWARD_LOCK : 0)| (onSd ? PackageParser.PARSE_ON_SDCARD : 0);PackageParser pp = new PackageParser();pp.setSeparateProcesses(mSeparateProcesses);pp.setDisplayMetrics(mMetrics);final PackageParser.Package pkg;try {pkg = pp.parsePackage(tmpPackageFile, parseFlags);} catch (PackageParserException e) {res.setError("Failed parse during installPackageLI", e);return;}// Mark that we have an install time CPU ABI override.pkg.cpuAbiOverride = args.abiOverride;String pkgName = res.name = pkg.packageName;if ((pkg.applicationInfo.flags&ApplicationInfo.FLAG_TEST_ONLY) != 0) {if ((installFlags & PackageManager.INSTALL_ALLOW_TEST) == 0) {res.setError(INSTALL_FAILED_TEST_ONLY, "installPackageLI");return;}}try {pp.collectCertificates(pkg, parseFlags);pp.collectManifestDigest(pkg);} catch (PackageParserException e) {res.setError("Failed collect during installPackageLI", e);return;}/* If the installer passed in a manifest digest, compare it now. */if (args.manifestDigest != null) {if (DEBUG_INSTALL) {final String parsedManifest = pkg.manifestDigest == null ? "null": pkg.manifestDigest.toString();Slog.d(TAG, "Comparing manifests: " + args.manifestDigest.toString() + " vs. "+ parsedManifest);}if (!args.manifestDigest.equals(pkg.manifestDigest)) {res.setError(INSTALL_FAILED_PACKAGE_CHANGED, "Manifest digest changed");return;}} else if (DEBUG_INSTALL) {final String parsedManifest = pkg.manifestDigest == null? "null" : pkg.manifestDigest.toString();Slog.d(TAG, "manifestDigest was not present, but parser got: " + parsedManifest);}// Get rid of all references to package scan path via parser.pp = null;String oldCodePath = null;boolean systemApp = false;synchronized (mPackages) {// Check whether the newly-scanned package wants to define an already-defined permint N = pkg.permissions.size();for (int i = N-1; i >= 0; i--) {PackageParser.Permission perm = pkg.permissions.get(i);BasePermission bp = mSettings.mPermissions.get(perm.info.name);if (bp != null) {// If the defining package is signed with our cert, it's okay. This// also includes the "updating the same package" case, of course.// "updating same package" could also involve key-rotation.final boolean sigsOk;if (!bp.sourcePackage.equals(pkg.packageName)|| !(bp.packageSetting instanceof PackageSetting)|| !bp.packageSetting.keySetData.isUsingUpgradeKeySets()|| ((PackageSetting) bp.packageSetting).sharedUser != null) {sigsOk = compareSignatures(bp.packageSetting.signatures.mSignatures,pkg.mSignatures) == PackageManager.SIGNATURE_MATCH;} else {sigsOk = checkUpgradeKeySetLP((PackageSetting) bp.packageSetting, pkg);}if (!sigsOk) {// If the owning package is the system itself, we log but allow// install to proceed; we fail the install on all other permission// redefinitions.if (!bp.sourcePackage.equals("android")) {res.setError(INSTALL_FAILED_DUPLICATE_PERMISSION, "Package "+ pkg.packageName + " attempting to redeclare permission "+ perm.info.name + " already owned by " + bp.sourcePackage);res.origPermission = perm.info.name;res.origPackage = bp.sourcePackage;return;} else {Slog.w(TAG, "Package " + pkg.packageName+ " attempting to redeclare system permission "+ perm.info.name + "; ignoring new declaration");pkg.permissions.remove(i);}}}}// Check if installing already existing packageif ((installFlags & PackageManager.INSTALL_REPLACE_EXISTING) != 0) {String oldName = mSettings.mRenamedPackages.get(pkgName);if (pkg.mOriginalPackages != null&& pkg.mOriginalPackages.contains(oldName)&& mPackages.containsKey(oldName)) {// This package is derived from an original package,// and this device has been updating from that original// name. We must continue using the original name, so// rename the new package here.pkg.setPackageName(oldName);pkgName = pkg.packageName;replace = true;if (DEBUG_INSTALL) Slog.d(TAG, "Replacing existing renamed package: oldName="+ oldName + " pkgName=" + pkgName);} else if (mPackages.containsKey(pkgName)) {// This package, under its official name, already exists// on the device; we should replace it.replace = true;if (DEBUG_INSTALL) Slog.d(TAG, "Replace existing pacakge: " + pkgName);}}PackageSetting ps = mSettings.mPackages.get(pkgName);if (ps != null) {if (DEBUG_INSTALL) Slog.d(TAG, "Existing package: " + ps);oldCodePath = mSettings.mPackages.get(pkgName).codePathString;if (ps.pkg != null && ps.pkg.applicationInfo != null) {systemApp = (ps.pkg.applicationInfo.flags &ApplicationInfo.FLAG_SYSTEM) != 0;}res.origUsers = ps.queryInstalledUsers(sUserManager.getUserIds(), true);}}if (systemApp && onSd) {// Disable updates to system apps on sdcardres.setError(INSTALL_FAILED_INVALID_INSTALL_LOCATION,"Cannot install updates to system apps on sdcard");return;}if (!args.doRename(res.returnCode, pkg, oldCodePath)) {res.setError(INSTALL_FAILED_INSUFFICIENT_STORAGE, "Failed rename");return;}if (replace) {replacePackageLI(pkg, parseFlags, scanFlags | SCAN_REPLACING, args.user,installerPackageName, res);} else {installNewPackageLI(pkg, parseFlags, scanFlags | SCAN_DELETE_DATA_ON_FAILURES,args.user, installerPackageName, res);}synchronized (mPackages) {final PackageSetting ps = mSettings.mPackages.get(pkgName);if (ps != null) {res.newUsers = ps.queryInstalledUsers(sUserManager.getUserIds(), true);}}}
这个方法先是解析了package包,然后做了大量签名和权限校验的工作,最终会走到
if (replace) {replacePackageLI(pkg, parseFlags, scanFlags | SCAN_REPLACING, args.user,installerPackageName, res);} else {installNewPackageLI(pkg, parseFlags, scanFlags | SCAN_DELETE_DATA_ON_FAILURES,args.user, installerPackageName, res);}
这两个方法分别是覆盖安装和安装新应用对应的具体执行.我们来看看installNewPackageLI()
2.3 installNewPackageLI()
private void installNewPackageLI(PackageParser.Package pkg,int parseFlags, int scanFlags, UserHandle user,String installerPackageName, PackageInstalledInfo res) {// Remember this for later, in case we need to rollback this installString pkgName = pkg.packageName;if (DEBUG_INSTALL) Slog.d(TAG, "installNewPackageLI: " + pkg);boolean dataDirExists = getDataPathForPackage(pkg.packageName, 0).exists();synchronized(mPackages) {if (mSettings.mRenamedPackages.containsKey(pkgName)) {// A package with the same name is already installed, though// it has been renamed to an older name. The package we// are trying to install should be installed as an update to// the existing one, but that has not been requested, so bail.res.setError(INSTALL_FAILED_ALREADY_EXISTS, "Attempt to re-install " + pkgName+ " without first uninstalling package running as "+ mSettings.mRenamedPackages.get(pkgName));return;}if (mPackages.containsKey(pkgName)) {// Don't allow installation over an existing package with the same name.res.setError(INSTALL_FAILED_ALREADY_EXISTS, "Attempt to re-install " + pkgName+ " without first uninstalling.");return;}}try {PackageParser.Package newPackage = scanPackageLI(pkg, parseFlags, scanFlags,System.currentTimeMillis(), user);updateSettingsLI(newPackage, installerPackageName, null, null, res);// delete the partially installed application. the data directory will have to be// restored if it was already existingif (res.returnCode != PackageManager.INSTALL_SUCCEEDED) {// remove package from internal structures. Note that we want deletePackageX to// delete the package data and cache directories that it created in// scanPackageLocked, unless those directories existed before we even tried to// install.deletePackageLI(pkgName, UserHandle.ALL, false, null, null,dataDirExists ? PackageManager.DELETE_KEEP_DATA : 0,res.removedInfo, true);}} catch (PackageManagerException e) {res.setError("Package couldn't be installed in " + pkg.codePath, e);}}
这个方法核心的步骤有两个:
PackageParser.Package newPackage = scanPackageLI(pkg, parseFlags, scanFlags,System.currentTimeMillis(), user);updateSettingsLI(newPackage, installerPackageName, null, null, res);
scanPackageLI负责安装,而updateSettingLI则是完成安装后的设置信息更新
2.4 scanPackageLI()
scanPackageLI()方法主要逻辑是由scanPackageDirtyLI()实现的,scanPackageDirtyLI()实在太长了,此处就不列出了,主要说下,这个方法实现了以下操作:
- 设置系统App的一些参数
- 校验签名
- 解析app的provider,校验是否与已有的provider冲突
- 32/64位abi的一些设置
- 四大组件的解析,注册
scanPackageDirtyLI()里面的操作确实是太多了,并不止这几点。如需更详细的信息还请查看源码。
另一方面,这个方法里,会调用到performDexOptLI(),其会去执行dexopt操作。
3. dexopt操作
Apk文件其实只是一个归档zip压缩包,而我们编写的代码最终都编译成了.dex文件,但为了提高运行性能,android系统并不会直接执行.dex,而是会在安装过程中执行dexopt操作来优化.dex文件,最终android系统执行的时优化后的’odex’文件(注意:这个odex文件的后缀也是.dex,其路径在data/dalvik-cache)。对于dalvik虚拟机,dexopt就是优化操作,而对于art虚拟机,dexopt执行的则是dex2oat操作,既将.dex文件翻译成oat文件。关于art和dex2oat的更多信息请看后文。
这里我们先来看看PMS的dexopt操作:
3.1 performDexOptLI()
这个方法的核心是
final int ret = mInstaller.dexopt(path, sharedGid, !isForwardLocked(pkg), pkg.packageName, dexCodeInstructionSet, vmSafeMode);
其作用就是调用PMS的mInstaller成员变量的dexopt操作。
3.2 Installer.dexopt
Installer类的dexopt方法又调用InstallerConnection类的dexopt方法,来看看这个方法:
public int dexopt(String apkPath, int uid, boolean isPublic, String pkgName,String instructionSet, boolean vmSafeMode) {StringBuilder builder = new StringBuilder("dexopt");builder.append(' ');builder.append(apkPath);builder.append(' ');builder.append(uid);builder.append(isPublic ? " 1" : " 0");builder.append(' ');builder.append(pkgName);builder.append(' ');builder.append(instructionSet);builder.append(' ');builder.append(vmSafeMode ? " 1" : " 0");return execute(builder.toString());}public synchronized String transact(String cmd) {if (!connect()) {Slog.e(TAG, "connection failed");return "-1";}if (!writeCommand(cmd)) {/** If installd died and restarted in the background (unlikely but* possible) we'll fail on the next write (this one). Try to* reconnect and write the command one more time before giving up.*/Slog.e(TAG, "write command failed? reconnect!");if (!connect() || !writeCommand(cmd)) {return "-1";}}if (LOCAL_DEBUG) {Slog.i(TAG, "send: '" + cmd + "'");}final int replyLength = readReply();if (replyLength > 0) {String s = new String(buf, 0, replyLength);if (LOCAL_DEBUG) {Slog.i(TAG, "recv: '" + s + "'");}return s;} else {if (LOCAL_DEBUG) {Slog.i(TAG, "fail");}return "-1";}}public int execute(String cmd) {String res = transact(cmd);try {return Integer.parseInt(res);} catch (NumberFormatException ex) {return -1;}}private boolean connect() {if (mSocket != null) {return true;}Slog.i(TAG, "connecting...");try {mSocket = new LocalSocket();LocalSocketAddress address = new LocalSocketAddress("installd",LocalSocketAddress.Namespace.RESERVED);mSocket.connect(address);mIn = mSocket.getInputStream();mOut = mSocket.getOutputStream();} catch (IOException ex) {disconnect();return false;}return true;}
由上面的几个方法可以知道,最终dexopt操作是通过socket的方式来跨进程通知守护进程installd,由其去执行dexopt操作。
3.3 commands::dexopt()
最终守护进程installd会调用Commands.c文件(位于/source/framework/native/cmds/installd)的dexopt方法。
int dexopt(const char *apk_path, uid_t uid, bool is_public,const char *pkgname, const char *instruction_set,bool vm_safe_mode, bool is_patchoat){struct utimbuf ut;struct stat input_stat, dex_stat;char out_path[PKG_PATH_MAX];char persist_sys_dalvik_vm_lib[PROPERTY_VALUE_MAX];char *end;const char *input_file;char in_odex_path[PKG_PATH_MAX];int res, input_fd=-1, out_fd=-1;......pid_t pid;pid = fork();if (pid == 0) {/* child -- drop privileges before continuing */if (setgid(uid) != 0) {ALOGE("setgid(%d) failed in installd during dexopt\n", uid);exit(64);}if (setuid(uid) != 0) {ALOGE("setuid(%d) failed in installd during dexopt\n", uid);exit(65);}// drop capabilitiesstruct __user_cap_header_struct capheader;struct __user_cap_data_struct capdata[2];memset(&capheader, 0, sizeof(capheader));memset(&capdata, 0, sizeof(capdata));capheader.version = _LINUX_CAPABILITY_VERSION_3;if (capset(&capheader, &capdata[0]) < 0) {ALOGE("capset failed: %s\n", strerror(errno));exit(66);}if (set_sched_policy(0, SP_BACKGROUND) < 0) {ALOGE("set_sched_policy failed: %s\n", strerror(errno));exit(70);}if (flock(out_fd, LOCK_EX | LOCK_NB) != 0) {ALOGE("flock(%s) failed: %s\n", out_path, strerror(errno));exit(67);}if (strncmp(persist_sys_dalvik_vm_lib, "libdvm", 6) == 0) {run_dexopt(input_fd, out_fd, input_file, out_path);} else if (strncmp(persist_sys_dalvik_vm_lib, "libart", 6) == 0) {if (is_patchoat) {run_patchoat(input_fd, out_fd, input_file, out_path, pkgname, instruction_set);} else {run_dex2oat(input_fd, out_fd, input_file, out_path, pkgname, instruction_set,vm_safe_mode);}} else {exit(69); /* Unexpected persist.sys.dalvik.vm.lib value */}exit(68); /* only get here on exec failure */} else {res = wait_child(pid);if (res == 0) {ALOGV("DexInv: --- END '%s' (success) ---\n", input_file);} else {ALOGE("DexInv: --- END '%s' --- status=0x%04x, process failed\n", input_file, res);goto fail;}}ut.actime = input_stat.st_atime;ut.modtime = input_stat.st_mtime;utime(out_path, &ut);close(out_fd);close(input_fd);return 0;fail:if (out_fd >= 0) {close(out_fd);unlink(out_path);}if (input_fd >= 0) {close(input_fd);}return -1;}
由上面的代码可以发现,installd在做了些操作后,fork出了一个新的进程,根据虚拟机的类型为libdvm或libart分别执行run_dexopt或run_dex2oat(如果为is_patchoat,则是run_patchoat)操作。
4. 更新权限信息
dexopt操作执行完后,installNewPackageLI()方法就会走到updateSettingsLI()来更新设置信息,而更新设置信息主要是权限信息,所以直接来看updatePermissionsLPw();
4.1 updatePermissionsLPw
private void updatePermissionsLPw(String changingPkg,PackageParser.Package pkgInfo, int flags) {// Make sure there are no dangling permission trees.Iterator<BasePermission> it = mSettings.mPermissionTrees.values().iterator();while (it.hasNext()) {final BasePermission bp = it.next();if (bp.packageSetting == null) {// We may not yet have parsed the package, so just see if// we still know about its settings.bp.packageSetting = mSettings.mPackages.get(bp.sourcePackage);}if (bp.packageSetting == null) {Slog.w(TAG, "Removing dangling permission tree: " + bp.name+ " from package " + bp.sourcePackage);it.remove();} else if (changingPkg != null && changingPkg.equals(bp.sourcePackage)) {if (pkgInfo == null || !hasPermission(pkgInfo, bp.name)) {Slog.i(TAG, "Removing old permission tree: " + bp.name+ " from package " + bp.sourcePackage);flags |= UPDATE_PERMISSIONS_ALL;it.remove();}}}// Make sure all dynamic permissions have been assigned to a package,// and make sure there are no dangling permissions.it = mSettings.mPermissions.values().iterator();while (it.hasNext()) {final BasePermission bp = it.next();if (bp.type == BasePermission.TYPE_DYNAMIC) {if (DEBUG_SETTINGS) Log.v(TAG, "Dynamic permission: name="+ bp.name + " pkg=" + bp.sourcePackage+ " info=" + bp.pendingInfo);if (bp.packageSetting == null && bp.pendingInfo != null) {final BasePermission tree = findPermissionTreeLP(bp.name);if (tree != null && tree.perm != null) {bp.packageSetting = tree.packageSetting;bp.perm = new PackageParser.Permission(tree.perm.owner,new PermissionInfo(bp.pendingInfo));bp.perm.info.packageName = tree.perm.info.packageName;bp.perm.info.name = bp.name;bp.uid = tree.uid;}}}if (bp.packageSetting == null) {// We may not yet have parsed the package, so just see if// we still know about its settings.bp.packageSetting = mSettings.mPackages.get(bp.sourcePackage);}if (bp.packageSetting == null) {Slog.w(TAG, "Removing dangling permission: " + bp.name+ " from package " + bp.sourcePackage);it.remove();} else if (changingPkg != null && changingPkg.equals(bp.sourcePackage)) {if (pkgInfo == null || !hasPermission(pkgInfo, bp.name)) {Slog.i(TAG, "Removing old permission: " + bp.name+ " from package " + bp.sourcePackage);flags |= UPDATE_PERMISSIONS_ALL;it.remove();}}}// Now update the permissions for all packages, in particular// replace the granted permissions of the system packages.if ((flags&UPDATE_PERMISSIONS_ALL) != 0) {for (PackageParser.Package pkg : mPackages.values()) {if (pkg != pkgInfo) {grantPermissionsLPw(pkg, (flags&UPDATE_PERMISSIONS_REPLACE_ALL) != 0,changingPkg);}}}if (pkgInfo != null) {grantPermissionsLPw(pkgInfo, (flags&UPDATE_PERMISSIONS_REPLACE_PKG) != 0, changingPkg);}}private void grantPermissionsLPw(PackageParser.Package pkg, boolean replace,String packageOfInterest) {final PackageSetting ps = (PackageSetting) pkg.mExtras;if (ps == null) {return;}final GrantedPermissions gp = ps.sharedUser != null ? ps.sharedUser : ps;HashSet<String> origPermissions = gp.grantedPermissions;boolean changedPermission = false;if (replace) {ps.permissionsFixed = false;if (gp == ps) {origPermissions = new HashSet<String>(gp.grantedPermissions);gp.grantedPermissions.clear();gp.gids = mGlobalGids;}}if (gp.gids == null) {gp.gids = mGlobalGids;}final int N = pkg.requestedPermissions.size();for (int i=0; i<N; i++) {final String name = pkg.requestedPermissions.get(i);final boolean required = pkg.requestedPermissionsRequired.get(i);final BasePermission bp = mSettings.mPermissions.get(name);if (DEBUG_INSTALL) {if (gp != ps) {Log.i(TAG, "Package " + pkg.packageName + " checking " + name + ": " + bp);}}if (bp == null || bp.packageSetting == null) {if (packageOfInterest == null || packageOfInterest.equals(pkg.packageName)) {Slog.w(TAG, "Unknown permission " + name+ " in package " + pkg.packageName);}continue;}final String perm = bp.name;boolean allowed;boolean allowedSig = false;if ((bp.protectionLevel&PermissionInfo.PROTECTION_FLAG_APPOP) != 0) {// Keep track of app op permissions.ArraySet<String> pkgs = mAppOpPermissionPackages.get(bp.name);if (pkgs == null) {pkgs = new ArraySet<>();mAppOpPermissionPackages.put(bp.name, pkgs);}pkgs.add(pkg.packageName);}final int level = bp.protectionLevel & PermissionInfo.PROTECTION_MASK_BASE;if (level == PermissionInfo.PROTECTION_NORMAL|| level == PermissionInfo.PROTECTION_DANGEROUS) {// We grant a normal or dangerous permission if any of the following// are true:// 1) The permission is required// 2) The permission is optional, but was granted in the past// 3) The permission is optional, but was requested by an// app in /system (not /data)//// Otherwise, reject the permission.allowed = (required || origPermissions.contains(perm)|| (isSystemApp(ps) && !isUpdatedSystemApp(ps)));} else if (bp.packageSetting == null) {// This permission is invalid; skip it.allowed = false;} else if (level == PermissionInfo.PROTECTION_SIGNATURE) {allowed = grantSignaturePermission(perm, pkg, bp, origPermissions);if (allowed) {allowedSig = true;}} else {allowed = false;}if (DEBUG_INSTALL) {if (gp != ps) {Log.i(TAG, "Package " + pkg.packageName + " granting " + perm);}}if (allowed) {if (!isSystemApp(ps) && ps.permissionsFixed) {// If this is an existing, non-system package, then// we can't add any new permissions to it.if (!allowedSig && !gp.grantedPermissions.contains(perm)) {// Except... if this is a permission that was added// to the platform (note: need to only do this when// updating the platform).allowed = isNewPlatformPermissionForPackage(perm, pkg);}}if (allowed) {if (!gp.grantedPermissions.contains(perm)) {changedPermission = true;gp.grantedPermissions.add(perm);gp.gids = appendInts(gp.gids, bp.gids);} else if (!ps.haveGids) {gp.gids = appendInts(gp.gids, bp.gids);}} else {if (packageOfInterest == null || packageOfInterest.equals(pkg.packageName)) {Slog.w(TAG, "Not granting permission " + perm+ " to package " + pkg.packageName+ " because it was previously installed without");}}} else {if (gp.grantedPermissions.remove(perm)) {changedPermission = true;gp.gids = removeInts(gp.gids, bp.gids);Slog.i(TAG, "Un-granting permission " + perm+ " from package " + pkg.packageName+ " (protectionLevel=" + bp.protectionLevel+ " flags=0x" + Integer.toHexString(pkg.applicationInfo.flags)+ ")");} else if ((bp.protectionLevel&PermissionInfo.PROTECTION_FLAG_APPOP) == 0) {// Don't print warning for app op permissions, since it is fine for them// not to be granted, there is a UI for the user to decide.if (packageOfInterest == null || packageOfInterest.equals(pkg.packageName)) {Slog.w(TAG, "Not granting permission " + perm+ " to package " + pkg.packageName+ " (protectionLevel=" + bp.protectionLevel+ " flags=0x" + Integer.toHexString(pkg.applicationInfo.flags)+ ")");}}}}if ((changedPermission || replace) && !ps.permissionsFixed &&!isSystemApp(ps) || isUpdatedSystemApp(ps)){// This is the first that we have heard about this package, so the// permissions we have now selected are fixed until explicitly// changed.ps.permissionsFixed = true;}ps.haveGids = true;}
由上面两个方法可以看到,在apk的安装时PMS会将该app的所有权限都记录下来并更新到PMS的mAppOpPermissionPackages成员变量里面,并判定是否授予该app请求的权限。
4.2 完成安装
还记得前面说过的在processPendingInstall方法在执行installPackageLi后会执行以下语句
if (res.returnCode == PackageManager.INSTALL_SUCCEEDED && doRestore) {// Pass responsibility to the Backup Manager. It will perform a// restore if appropriate, then pass responsibility back to the// Package Manager to run the post-install observer callbacks// and broadcasts.IBackupManager bm = IBackupManager.Stub.asInterface(ServiceManager.getService(Context.BACKUP_SERVICE));if (bm != null) {if (DEBUG_INSTALL) Log.v(TAG, "token " + token+ " to BM for possible restore");try {bm.restoreAtInstall(res.pkg.applicationInfo.packageName, token);} catch (RemoteException e) {// can't happen; the backup manager is local} catch (Exception e) {Slog.e(TAG, "Exception trying to enqueue restore", e);doRestore = false;}} else {Slog.e(TAG, "Backup Manager not found!");doRestore = false;}}
我也不是很清楚为什么系统会调用IBackupManager的restoreAtInstall方法,不过发现在BackupManagerService的restoreAtInstall方法中会有以下代码:
...if (skip) {// Auto-restore disabled or no way to attempt a restore; just tell the Package// Manager to proceed with the post-install handling for this package.if (DEBUG) Slog.v(TAG, "Finishing install immediately");try {mPackageManagerBinder.finishPackageInstall(token);} catch (RemoteException e) { /* can't happen */ }}...
最终restoreAtInstall方法又会调用PMS的finishPackageInstall方法,而此方法最终会发送Intent.ACTION_PACKAGE_ADDED广播,apk的安装就到到此结束了。