- 示例1,基本使用
- 示例2,使用字段匹配路由
静态分页是指页面的分页参数使用的是路由传参,这种场景下分页对象与Web Server的路由设计耦合性比较大。
示例1,基本使用
package mainimport ("github.com/gogf/gf/g""github.com/gogf/gf/g/os/gview""github.com/gogf/gf/g/net/ghttp""github.com/gogf/gf/g/util/gpage")func main() {s := ghttp.GetServer()s.BindHandler("/page/static/*page", func(r *ghttp.Request){page := gpage.New(100, 10, r.Get("page"), r.URL.String(), r.Router)buffer, _ := gview.ParseContent(`<html><head><style>a,span {padding:8px; font-size:16px;}div{margin:5px 5px 20px 5px}</style></head><body><div>{{.page1}}</div><div>{{.page2}}</div><div>{{.page3}}</div><div>{{.page4}}</div></body></html>`, g.Map{"page1" : page.GetContent(1),"page2" : page.GetContent(2),"page3" : page.GetContent(3),"page4" : page.GetContent(4),})r.Response.Write(buffer)})s.SetPort(8199)s.Run()}
在该示例中,我们需要用到分页对象New方法的第五个参数,route...string,该参数是当前请求的路由规则。我们这里可以通过r.Router.Uri方式将路由规则传递给分页对象。其中,ghttp.Request.Router是与当前请求匹配的路由对象,包含路由规则等相关信息,在分页对象中处理分页参数时,我们只会用到Uri属性。
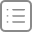
执行后,我们手动访问http://127.0.0.1:8199/page/static/6页面的结果如下:
示例2,使用字段匹配路由
package mainimport ("github.com/gogf/gf/g""github.com/gogf/gf/g/os/gview""github.com/gogf/gf/g/net/ghttp""github.com/gogf/gf/g/util/gpage")func main() {s := g.Server()s.BindHandler("/:obj/*action/{page}.html", func(r *ghttp.Request){page := gpage.New(100, 10, r.Get("page"), r.URL.String(), r.Router)buffer, _ := gview.ParseContent(`<html><head><style>a,span {padding:8px; font-size:16px;}div{margin:5px 5px 20px 5px}</style></head><body><div>{{.page1}}</div><div>{{.page2}}</div><div>{{.page3}}</div><div>{{.page4}}</div></body></html>`, g.Map{"page1" : page.GetContent(1),"page2" : page.GetContent(2),"page3" : page.GetContent(3),"page4" : page.GetContent(4),})r.Response.Write(buffer)})s.SetPort(8199)s.Run()}
该示例的路由规则更加灵活,其中使用了{page}字段匹配规则,用于获取当前的分页页码信息。执行后,我们按照路由规则随意访问一个URL如:http://127.0.0.1:8199/order/list/6.html,结果如下图所示: